| vlsitechnology.org /IR drop /2W power with blocks improved |
Example Calculation of Power Strap Width with 6LM, 30% RAM, 20% Analog, Different Resistivities and Widths, 2W Core Power |
IR Drop
- IR drop problem
- Power delivery
- 10% power straps
- standard cell
- chip illustration
- calculate width
- conductivity calc.
- strap width
- 1W core power
- 2W core power
- fixed blocks
- 1W 30% blocks
- 2W 30% RAM, 20% analog
- upper power straps
- die size impact
- examples' die size
- reducing impact
- 1W power best
- 2W power best
- 1W best 30% blocks
- 2W best RAM, analog
- summary of method
- conclusions
Derivations
Step 1: Calculate the voltage on the supply pad Vpad:
| Vpad = | Vddmin-2×Ipad×(Rlead+Rbond+Rpad) |
| = | 1.164 - 2 × 0.05 × (0.025 + 0.0125 + 0.05) |
| = | 1.155V |
Step 2: Calculate the reference power supply conductance G:
| G = | 7 |
| 4×r(2) | |
| = | 7 / (4 × 0.07) |
| = | 25 mhos |
Step 3: Set out the values of j(n), k(n) and m(n) for each metal layer, and use these to calculate the value of L.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ¹78% = .07/.09; ²350% = .07/.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
From which:
| L = | j(1)×k(1)×(1-ps)×(1-(1-p)×m(1)) + |
| j(2)×k(2)×(1-(1-p)×m(2)) + | |
| j(3)×k(3)×(1-(1-p)×m(3)) + | |
| j(4)×k(4)×(1-(1-p)×m(4)) + | |
| j(5)×k(5)×(1-(1-p)×m(5)) + | |
| j(5)×k(6)×(1-(1-p)×m(6)) |
We use the table below to iterate Step 3 to a value for L, Step 4 to a value for P(S) and Step 5 to a value for p, starting with p=0.
| iter- ation |
estimated p px‑1 |
Step 3 L |
Step 4 P(S) |
Step 5 new p px |
delta p p (px‑px‑1)÷px |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00% | 7.801 | 0.203 | 9.83% | 100.000% |
| 2 | 9.83% | 8.096 | 0.223 | 9.36% | -4.942% |
| 3 | 9.36% | 8.082 | 0.222 | 9.38% | 0.224% |
| 4 | 9.38% | 8.083 | 0.222 | 9.38% | -0.010% |
| 5 | 9.38% | 8.083 | 0.222 | 9.38% | 0.000% |
Let us compare this solution with the previous one assuming that our metal-1 to metal-4 Vdd and Vss power straps are 5.5µm wide and metal-5 and metal‑6 straps are 11µm wide.
| Design Attribute | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Ptot | core power consumption | 2W |
| ps | the fraction of metal-1 in the standard cells dedicated to power supplies | 22% (for vsclib) |
| r(1) | metal-1 resistivity measured in ohms per square | 0.09Ω per sq. |
| r(2-5) | the resistivity of metal layers 2-5 measured in ohms per square | 0.07Ω per sq. |
| r(6) | metal-6 resistivity measured in ohms per square | 0.02Ω per sq. |
| m(1-4) | percentage of metal layers 1-4 blocked to power straps | 50% |
| m(5-6) | percentage of metal layers 5-6 blocked to power straps | 20% |
| Vdd | the nominal supply voltage | 1.2V |
| Vddmin | the minimum supply voltage, 3% less than the nominal | 1.164V |
| Vmin | the desired voltage at the centre of the die, typically 10% less than the nominal | 1.08V |
| Ipad | the current per supply pad | 50mA |
| Rlead | the resistance of the package leadframe | 25mΩ |
| Rbond | the resistance of a double bond wire | 12.5mΩ |
| Rpad | the resistance of two parallel supply pads | 50mΩ |
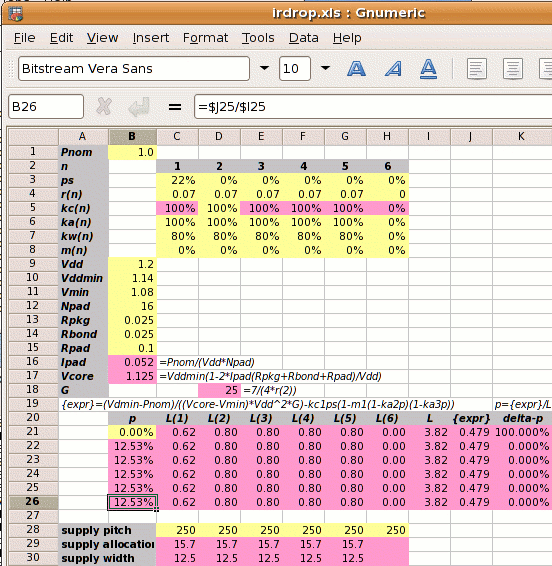
Using a spreadsheet to iterate to the solution.
| p | width m1-m4 |
width m5 |
width m6 |
horizontal pitch |
vertical pitch |
core side mm |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous power strap solution | 16.36% | 5.5um | 5.5um | 11um | 134um | 67um | 9.129 |
| New power strap solution | 9.38% | 5.5um | 11um | 11um | 234um | 117um | 8.608 |
The new solution has allowed the vertical power strap pitch to go up from one every 67µm to one every 117µm. The core side is 520µm less and the core area is 11% less than the first solution, due to double bonding of supply pads, tighter Vddmin spec and wider metal-5 straps.